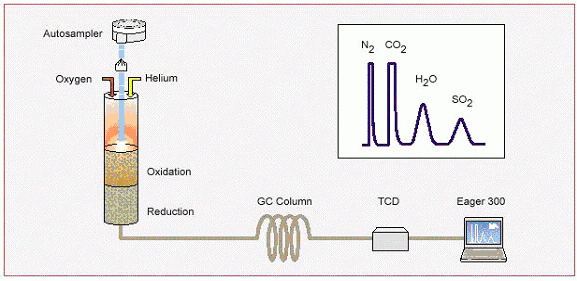
The elemental analysis technique, based on the complete and instantaneous oxidation of the sample (combustion) and subsequent determination of the combustion gases by means of a thermal conductivity detector, is an essential technique for the synthesis researcher (chemical, pharmaceutical, etc.), as it provides data that contribute to the confirmation of the structure of a newly prepared compound. It is also very useful in the analysis of soils, marine samples and, in general, in controlling the identity and purity of any type of sample containing the elements C, N, H, S and O.
Its main applications are:
- Identification of the purity of newly synthesised compounds: organic, organometallic, halogenated samples.
- Determination of C, H, N, S and O content in petrochemical derivatives: fuels, petrol, oils, cokes, etc.
- Analysis of vegetation, wood, algae, etc.
- Food analysis (nitrogen/protein ratio).
Depending on the quantity and homogeneity of the sample, the analysis will be carried out in microanalysis (1-20 mg in the CACTUS of Santiago de Compostela) or in macroanalysis (50-1000 mg in the CACTUS of Lugo).
Determination of total organic carbon
The selective determination of organic matter in a solid sample is possible after acidification with HCI.
Acidification is performed in a silver capsule where carbonates react (CO₂ is released) and the remaining organic matter is dried at 80 °C for complete removal of carbonates and water.
The Total Organic Carbon (TOC) of the sample is then determined with the standard analytical conditions of the analyser.
Generally, the untreated sample is also analysed to determine the Total Carbon (TC).
- Type of sample: soils, sediments, compost, etc.
- Size of the sample: 20 - 30 mg
Unidade de Análise Instrumental
- Edificio de Apoio á Investigación (CACTUS) Lugo
- Campus Lugo s/n, 27002Lugo
- 982 822 816 (Responsable da Unidade)
- 982 822 818