Crude oil recovery test equipment
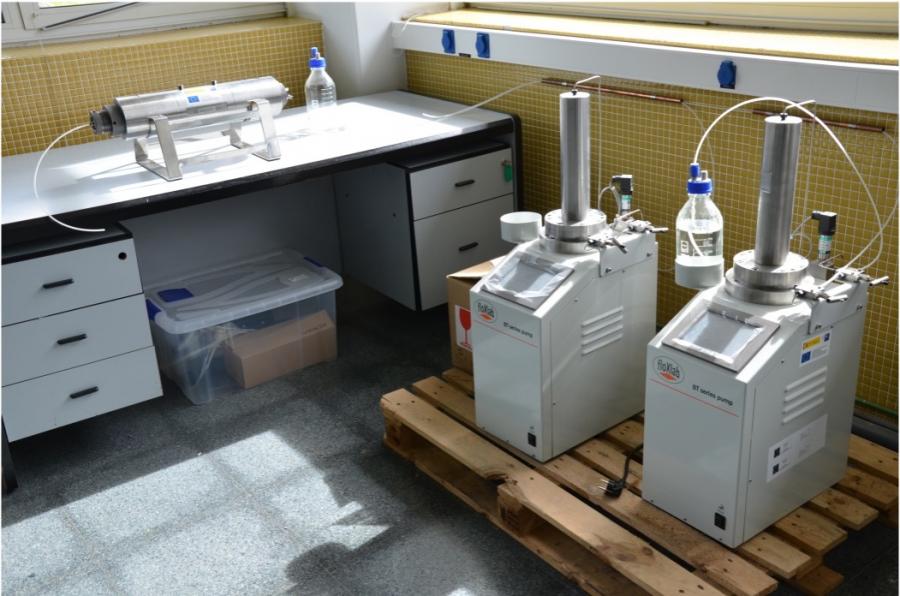


Experimental setup Core Holder Pressure Cylinder, consisting of:
- The Core Holder cylinder which is designed to store rock samples that are subjected to reservoir conditions (pressure and temperature) and because of this can withstand high pressures. A rock sample, usually taken from an actual reservoir, is inserted into the metal core holder.
An Edwards vacuum pump, with its vacuum trap system, to remove air from the pores of the core rock. - An Enerpac hand pressure pump, with pressure measurement system, for the pressurised oil sealing of the rock in the core-holder.
- Two Vinci-technologies floXlab piston pumps, one to initially drive the crude oil to soak the rock and a second pump to drive the chemical formulation under study for the extraction of the crude oil. They contain the tanks for the crude sample and chemical formulation
Funded by:
FEDER/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades – Agencia Estatal de Investigación/ _Proyecto CTQ2015-68496-P
Separation process equipment: vapour-liquid equilibrium
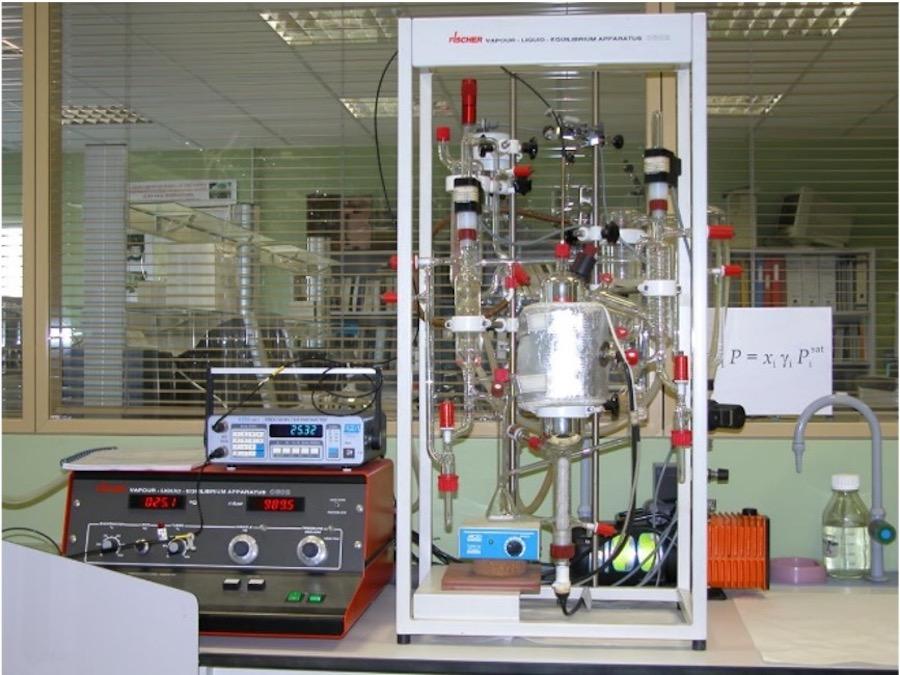

The LABODEST VLE 602 distiller, also called equilibrium distiller, is an apparatus for determining vapour-liquid equilibrium data. The vapour-liquid equilibrium of binary and multicomponent mixtures forms an essential basis for the determination of the theoretical plates necessary for the evaluation of separation processes. In particular, the additional evaluation of the theoretically additional temperature and pressure dependence of the phase equilibrium is insufficient in everyday practice, so that the experimental determination of VLE data is still required also in the overpressure range.
Equipped with :
- Universal glass apparatus, complete with silver-plated vacuum mantle, cooler, circulation evaporator and vacuum-sealed screws for taking samples by means of a syringe, with working certificate "Operating pressure".
- 1 immersion heater 350 W, with special surface finish to prevent shocks
- 1 magnetic stirrer for thorough mixing
- 10 end receivers with screw caps
- 1 filling funnel with PTFE key
- 2 solenoid coils
- 1 liquid temperature sensor Pt-100, with connecting cable and plug
- 1 vapour temperature sensor Pt-100, complete with connecting cable and plug
Equipment for separation processes: liquid-liquid equilibrium
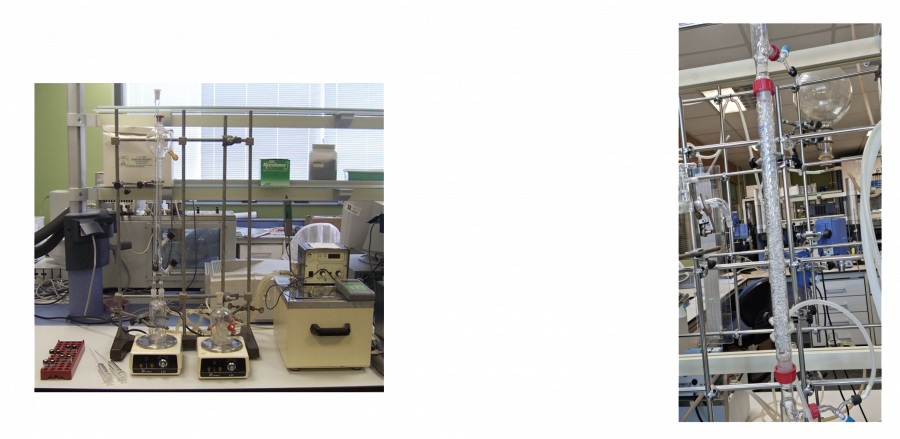

Experimental setup thermostated equilibrium cells for determination of liquid-liquid equilibrium data and packed column to study L-L extraction processes.
Liquid-liquid extraction is a very useful method to separate components of a mixture. The success of this method depends on the difference in solubility of the compound to be extracted in two different solvents. When a compound is shaken with two immiscible solvents, the compound is distributed between the two solvents. At a given temperature, the ratio of concentrations of the compound in each solvent is always constant, and this constant is called the distribution or partition coefficient (K = concentration in solvent 2 / concentration in solvent 1). Thermostatised equilibrium cells allow the calculation of these distribution coefficients, which are very useful for the selection of solvents.
The L-L extraction apparatus allows the extraction of one or more components continuously with a solvent to be studied. The contact takes place inside a vertical packed column, in which the two phases circulate in countercurrent.
Photo-reaction equipment
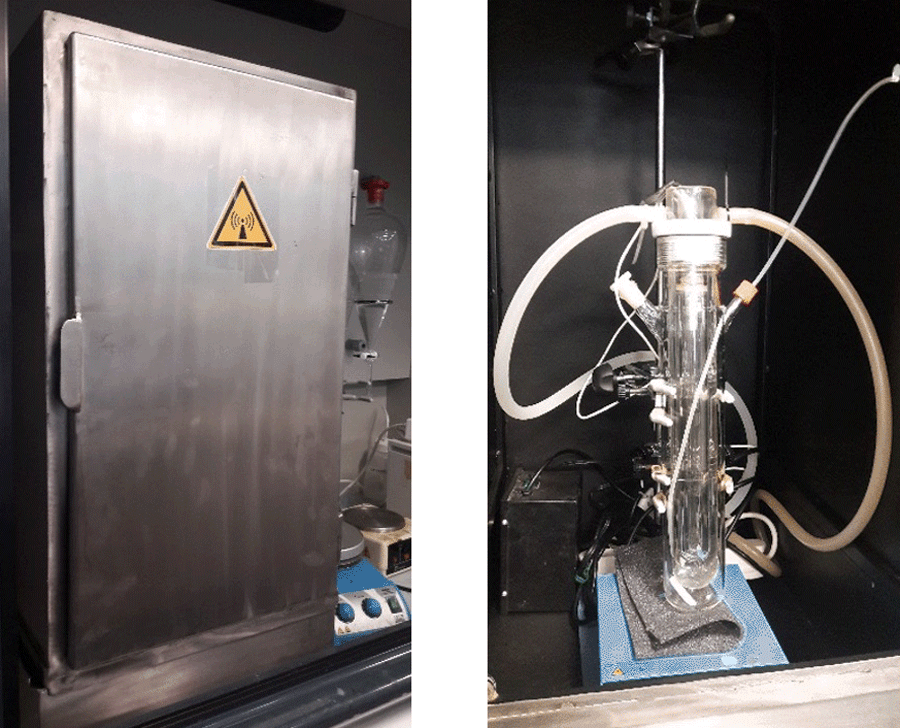
A photoreactor is a chemical reactor that uses light as an energy source to trigger a certain chemical reaction, usually using ultraviolet light due to its high energy content. The photoreactor is a batch reactor used in the field of photochemistry for simple, preliminary tests with a reaction volume of about 200 ml. The radiation source is located in the central axis of the reactor to achieve an optimal use of the emitted photons, while avoiding overheating which could affect its performance by the use of a cooling jacket. The larger optical path of the reactor (>2 cm) allows the use of conventional magnetic stirrers for solution mixing. As a general rule, this type of stirring is sufficient for reaction feasibility tests as a first step for further developments. Parts of the photoreactor and characteristics:
- Glass sample vessel (200 ml)
- Ultraviolet (UV) lamp, pen ray lamp, low-pressure mercury lamp
- Magnetic stirrer and stir bar
- Cooling system (quartz jacket)
- Sample inlets
Equipment for separation processes: gas-liquid equilibrium
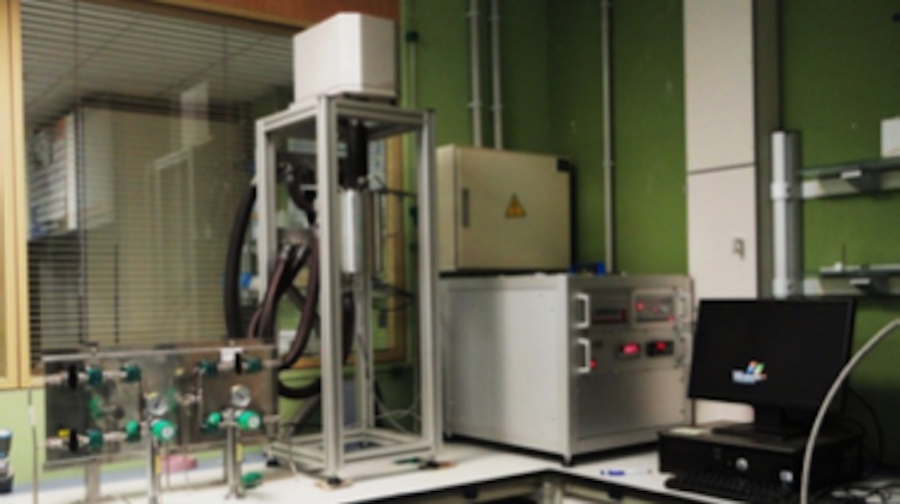

Gravimetric instrument featuring a patented magnetic suspension balance that allows adsorption measurements to be made in high pressure or vacuum environments.
Samples can be measured in the presence of a variety of gases or vapours over a wide temperature range. A flexible selection of dosing and mixing devices provide precise control of the composition and pressure of the reaction atmosphere.
In many processes, toxic and/or corrosive gases are generated or used. Adsorption is usually the method of choice for separating or cleaning mixtures containing these gases. Adsorption isotherms for all gases involved are the basis for the proper design of adsorption cleaning processes and materials. Because the design of this equipment completely isolates the reaction atmosphere from the surroundings, it allows adsorption measurements with corrosive and toxic gases to provide adsorption isotherms for material and process development.
Nanoparticle characterisation equipment
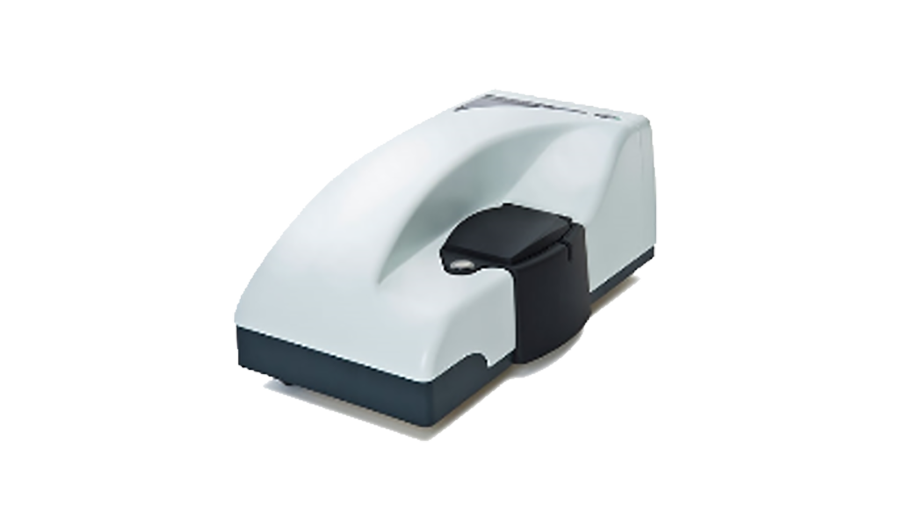

The Zetasizer Nano ZS is a high performance two-angle particle size and molecular size analyser for enhanced aggregate detection and measurement of small or dilute samples, and samples at very low or high concentration using dynamic light scattering with "NIBS" optics.
Size Measurement
- Maximum particle size range (diameter): 0.3 nm to 10 µm
- Minimum sample volume: 12 µl
- Maximum sample concentration: Up to 40% w/v
Potential Z measurement
- Particle size range (diameter): 3.8 nm to 100 µm
- Potential Z-range: no effective limitation.
- Electrophoretic mobility range: Minimum 0, no practical upper limit.
- Conductivity range: 0 to 200 mS/cm
- Sample concentration range: Up to 40% w/v
Thermal characterisation equipment
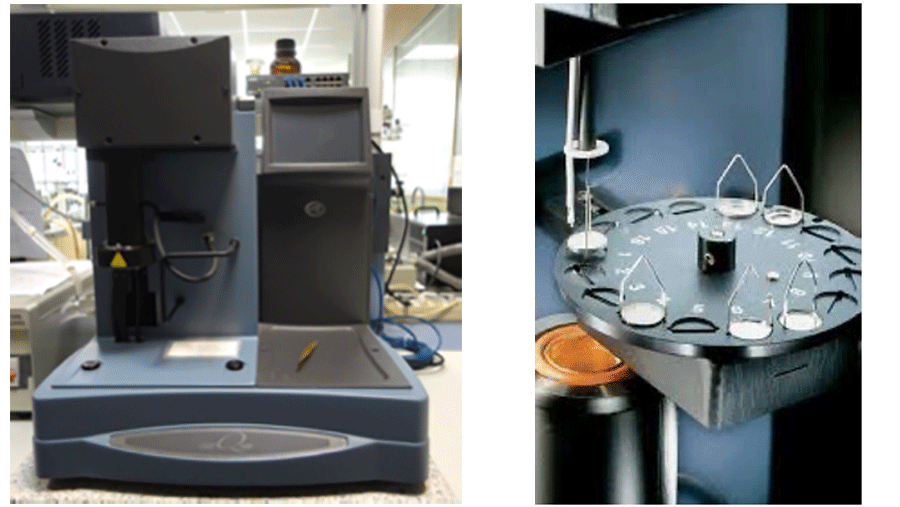

The TA Instruments Thermogravimetric Analyser (TGA) is a weight change analysis instrument, used in conjunction with a TA Instruments thermal analysis controller and associated software, to form a thermal analysis system.
The thermogravimetric analyser measures the amount and rate of weight change in a material, either as a function of increasing temperature, or isothermally as a function of time, in a controlled atmosphere. It can be used to characterise any material that exhibits a weight change and can detect phase changes due to decomposition, oxidation or dehydration. This information helps the scientist or engineer identify the percentage weight change and correlate chemical structure, processing and end-use performance.
Its controller is a computer that performs the following functions:
- Provides an interface between you and the analytical instruments
- Allows you to set up experiments and enter constants
- Stores experimental data
- Runs data analysis programs
Thermal characterisation equipment
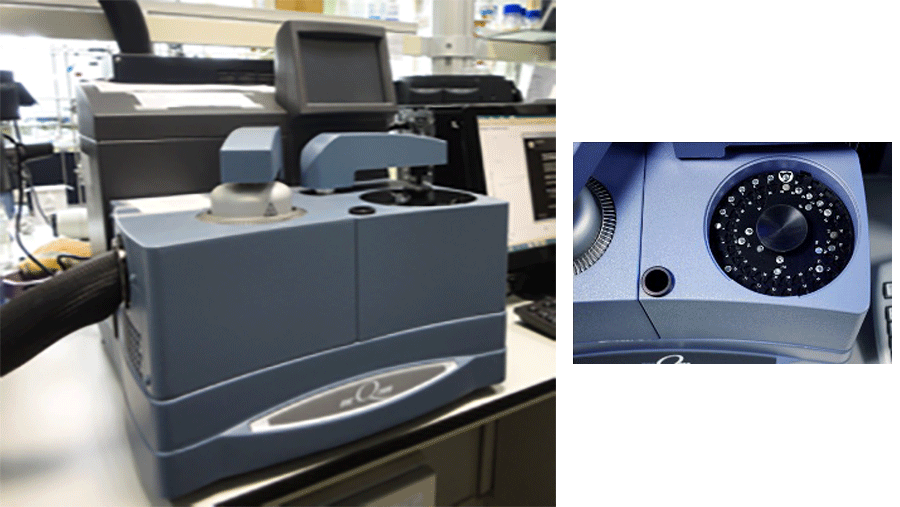

DCS measures the temperatures and heat fluxes associated with thermal transitions in a material. Properties measured by DSC techniques include heat capacity at different temperatures, parameters of glass transitions, phase changes (melting, crystallisation), product stability and curing kinetics.
TA Instruments Q100 features a unique oven design and heat flow measurement principle. A simplified descendant of the original power compensation DSC and a close relative of the DTA (differential thermal analysis) instruments, this DSC is suitable for accurate measurement of the temperature range of a thermal transition. The heat and heat capacity determinations are only semi-quantitative (the manufacturer does not specify the calorimetric accuracy). However, the less processed output signal in the heat flow design better reflects the shape of the narrow features in the calorimetric curves. In addition, temperature modulation, TA Instruments' signature technique, makes this DSC an instrument of choice if a complete analysis of the reversible and irreversible components in a given thermal transition is desired.
Thermophysical characterisation equipment
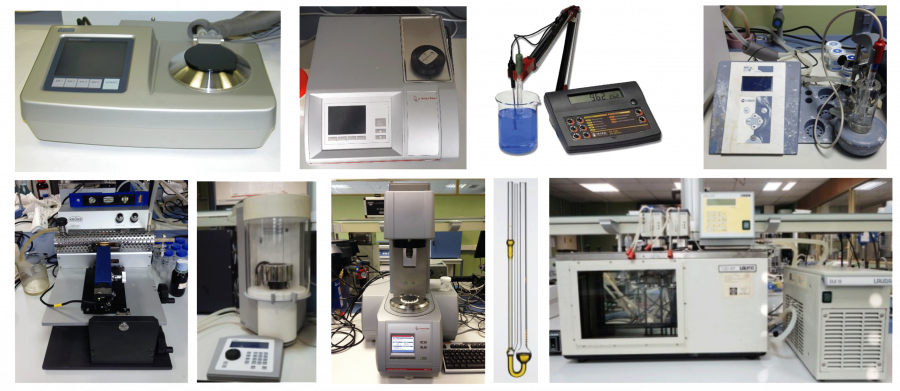
- Densimeter for liquids
- Refractometer
- Conductivity meter
- Tensiometers for liquids
- Capillary viscometers
- Rheometer
- pH meter
Compositional analysis equipment
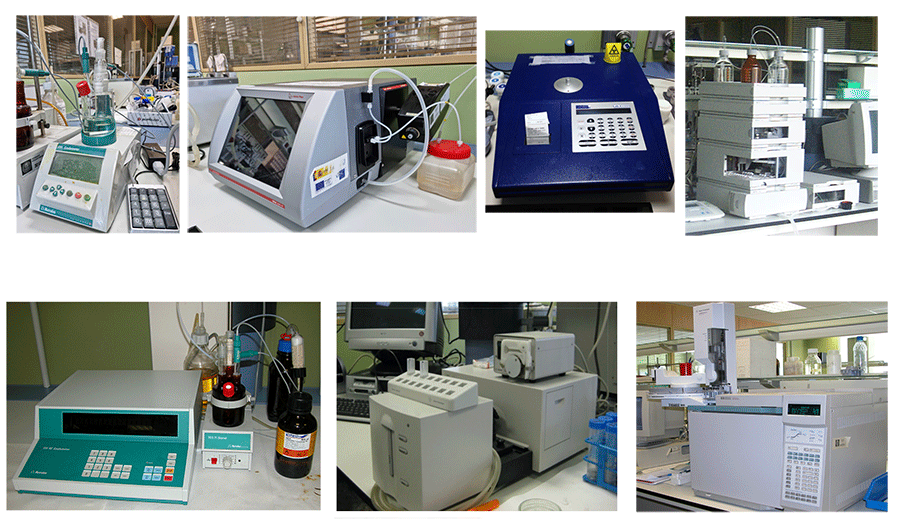

- High Performance Liquid Chromatograph (HPLC)
- Gas Chromatograph (GC)
- Coulometer (Karl-Fischer titrator)
- UV-visible spectrophotometer
- Sulphur analyser
Other equipment:
- Centrifuge
- Autoclave
- Mufla
- pH-meter
- Sonicators
- High vacuum pumps
- Magnetic stirring plates
- Thermostatic orbital shaker
- Analytical balances